Study Set Content:
For the RBC's to survive for 120 day lifespan, the following conditions are necessary:
(a)the red cell membrane must be deformed
(b)hemoglobin structure and function must be adequate
(c) the red cell metabolic pathways must be active
old RBC's are removed by
splenic macrophages
immature RBCs are less deformable
Select the Correct Answer:
Functions of RBC Membrane
- Separates intracellular from extracellular fluid
- Allows nutrient and ion passage selectively (Selective Permeability)
- Allows the cell to deform when needed
o Influenced by Cell shape Cytoplasmic Viscosity Membrane deformability and stability
Cell surface area of RBC is greater than the cell volume
Select the Correct Answer:
Membrane composition
-Semi-permeable lipid bilayer supported by a mesh-like cytoskeleton
-52 % CHON, 40 % lipids, 8 % CHO
-Over 300 RBC antigens have been identified in the membrane
glycolipids make up the surface antigen
Select the Correct Answer:
2 kinds of proteins of erythrocyte membrane
: Integral proteins and Peripheral proteins
membrane proteins that extend from the outer surface and traverse the entire membrane to the inner cytoplasmic site of RBCs. Embedded on lipid bilayers.
Integral proteins
situated right beneath the inner leaflet.
Peripheral proteins
outer layer of membrane
Outer leaflet
inner layer of membrane
Inner leaflet
Lipid composition
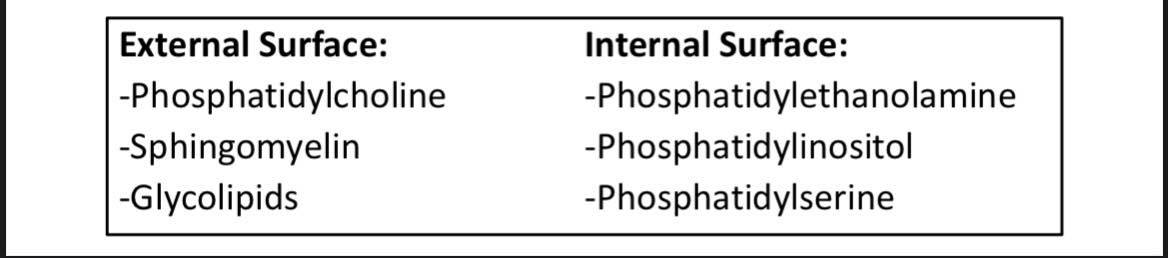
- Phospholipids and unesterified cholesterol are present in nearly equimolar quantities
- Free fatty acids and glycolipids are present in small quantities.
Phospholipids that are situated on the outer leaflet are collectively called
Choline Phospholipids
represent the controlling points in the major pathways of lipid renewal
Choline Phospholipids
also known as flippase. It functions to help the phospholipid to easily enter the membrane.
Aminophospholipid translocase (ATP dependent enzyme)
are the gateways in the entry of phospholipids. Those phospholipids need enzyme for entry and these enzymes are ATP-dependent
Phosphatidylcholine and Sphingomyelin
maintains the precise lipid pattern that is critical in normal survival of RBC in circulation.
Aminophospholipid
Inner leaflet has negative charge, the outer leaflet is still negative charge but is not from the phospholipid
Select the Correct Answer:
Negative charge phospholipid in the inner leaflet of the aged RBC if will be flipped will result in
phagocytosis
